The effects of 17 Beta-Estradiol primed mesenchymal stem cells on the biology of co-cultured neutrophil
Nasim Rahmani-Kukia, Ardeshir Abbasi, Seyyed Meysam Abtahi Froushani, Shahab Shahgaldi, Pooneh Mokarram
Abstract
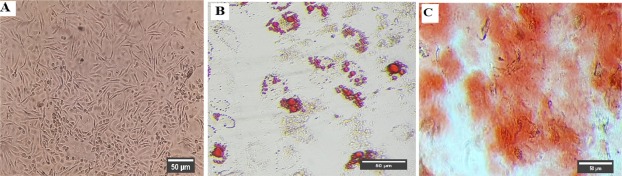
Objectives: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can influence immune effector cells. It is proved that MSCs respond to various Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands, which could ultimately result in changes in their immunomodulatory effects. Neutrophils play an essential role in the first line defense system and their function can be regulated by MSCs. Estrogen is a female hormone that contributes to sex differences in several immune-related diseases. With regard to the stated facts, this research aims to elucidate the effects of estrogen treatment on the ability of TLR4-primed MSCs to regulate neutrophil functions.
Methods: Following isolation and characterization, MSCs were stimulated with LPS as a TLR4 ligand and subsequently incubated with different concentrations (0, 10, 20 and 40 nM) of estrogen for 48 hrs. Then, MSCs were co-cultured with neutrophils to investigate the vitality and function of the co-cultured neutrophils.
Results: Our results indicated that TLR4-primed MSCs could decrease the viability and neutral red uptake potential of co-cultured neutrophils. Furthermore, neutrophils co-cultured with TLR4-primed MSCs exhibited a decrease in the respiratory burst intensity after being challenged with opsonized yeast. Interestingly, treating TLR4-primed MSCs with estrogen reversed the observed alterations in neutrophil functions.
Conclusion: It appears that estrogen can alter the interaction between MSCs and neutrophils.
برای مطالعه مقاله لطفا اینجا را کلیک کنید.

نظر دهید